Instagram’s Friend Map: A Social Feature with Serious Privacy Risks
Instagram’s recent introduction of the “Friend Map” feature was promoted as a fun and interactive way for users to see where friends are and discover new hangout spots. However, the rollout has been met with immediate concern from privacy advocates and cybersecurity experts, who warn that the implications extend far beyond casual socializing.
How Friend Map Works
When enabled, Instagram’s Friend Map collects two primary types of location data, creating a timestamped history of user movements. Although it does not provide continuous GPS tracking, repeated location check-ins can reveal detailed patterns, such as home and work addresses, travel routes, and frequently visited venues. All this information is stored centrally on Meta’s servers, which also support other company platforms like Facebook and Messenger.
Meta has not clarified how long it retains this data, instead stating it keeps information “as long as necessary” for service delivery, analytics, compliance, and commercial purposes. Unlike some security-first location services, Instagram’s Friend Map data is not end-to-end encrypted, meaning Meta and potentially its employees can access it. This centralization makes the data a lucrative target for cybercriminals, as a breach could expose not just usernames and passwords, but also detailed location histories for millions of users.
Integration with Meta’s Ad Ecosystem
Instagram’s location data is not siloed. Because it is integrated into Meta’s broader advertising infrastructure, data from Friend Map can be cross-referenced with a user’s browsing history, purchase activity, and demographic profile. This allows advertisers to target users with high precision—such as reaching people who visit a specific gym or coffee shop at certain times. While this enables granular marketing, the same data could be used for more nefarious purposes, such as targeted scams or disinformation campaigns.
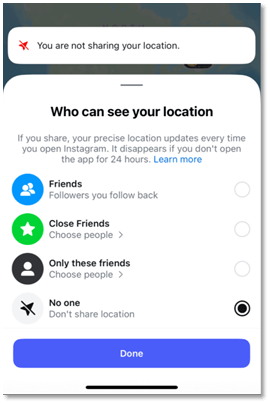
Physical and Digital Security Risks
The risks associated with location sharing on Instagram fall into two main categories—physical and digital—and often overlap. On the physical side, sharing real-time or historical location data can enable stalking, harassment, or in-person attacks. Patterns gleaned from check-ins may reveal a user’s daily commute, favorite venues, or jogging routes, information that could be exploited by criminals or stalkers. Social media location tags have also been used to identify when someone is away from home, potentially aiding in burglaries. For minors, the risks are even more acute, as predators can leverage location visibility to identify and approach vulnerable users.
Digitally, location data is a powerful tool for profiling. Meta’s advertising systems can merge it with other personal data to build comprehensive user profiles for targeted advertising. This opens the door to scams, phishing attempts, and manipulative content tailored to users’ inferred habits, political beliefs, or health conditions. The same information that helps advertisers predict coffee habits could help attackers identify when and how to exploit a user.
Comparisons with Other Location-Sharing Services
Instagram’s Friend Map is not the first location-sharing feature on the market. Apple’s Find My and Snapchat’s Snap Map offer similar services, but with key differences. Apple’s Find My is widely regarded as the most secure, using end-to-end encryption so that only approved contacts can access location data. Apple itself cannot view this information, and it is not used for advertising or social engagement.
Snapchat’s Snap Map is also opt-in, but has experienced incidents of misuse, including stalking and harassment, even when privacy features like Ghost Mode are enabled. Instagram Friend Map differs in several significant ways. First, it is fully integrated into Meta’s data ecosystem, linking location history to a much broader range of personal information. Second, Meta’s business model incentivizes the collection and analysis of such data for advertising. Third, Meta has experienced multiple data breaches in recent months, making its infrastructure an attractive target for cybercriminals seeking detailed user profiles.
Emerging Threats and Industry Response
Security analysts have already observed increased interest in Instagram Friend Map from malicious actors. Within days of the feature’s launch, discussions about its exploitation appeared on underground forums. The interconnected nature of Meta’s platforms means that a compromise in one service, such as Facebook or Messenger, could potentially expose location data from Instagram as well, significantly expanding the attack surface compared to standalone apps.
Balancing Social Utility and Safety
While Instagram’s Friend Map offers a novel way for users to connect and discover new places, it also introduces considerable risks related to privacy, safety, and data security. Users should weigh the social benefits against the potential for unwanted profiling, targeted attacks, and data breaches. Enabling Friend Map is a personal decision, but one that should be made with full awareness of the potential consequences and the limitations of Meta’s privacy protections.
Source: Original source